Introduction to Pneumonia
Posted March. 01, 2024 by Dr. Aniruddha Dharmadhikari
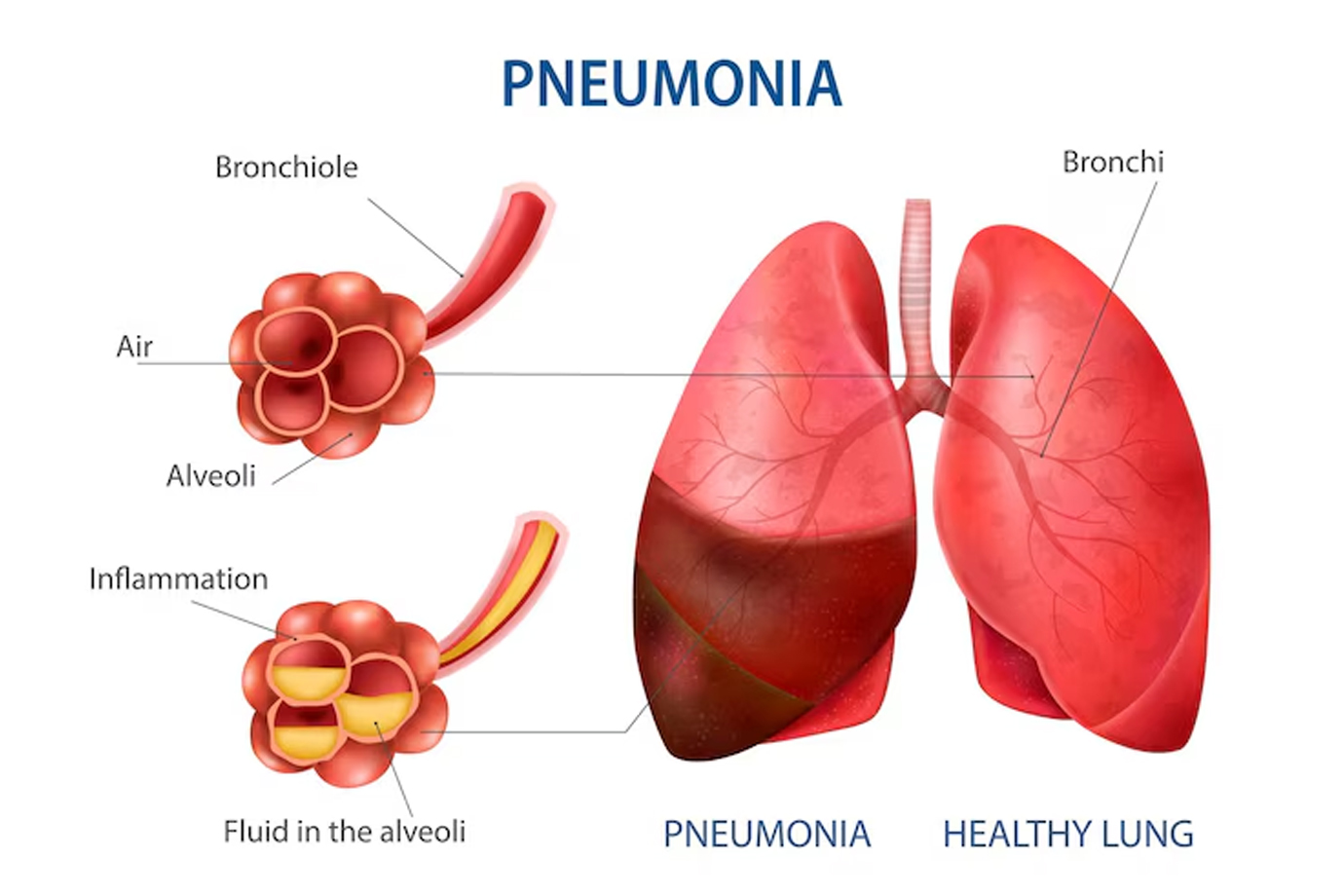
Pneumonia, a severe respiratory infection, profoundly impacts the lungs It can be caused by various factors including bacteria, viruses, fungi, or even chemicals. Pneumonia develops when the air sacs in the lungs become inflamed and accumulate fluid, leading to breathing difficulties. Common symptoms of pneumonia include cough, chest pain, fever, difficulty breathing, fatigue, and in severe cases, bluish lips or nails. It can affect people of all ages, but infants, young children, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems are at a higher risk. Early diagnosis is crucial for prompt treatment and to prevent complications.
Physical examination, chest X-rays, and laboratory tests are typically used to diagnose pneumonia. Treatment options include antibiotics (for bacterial pneumonia), antiviral medications (for viral pneumonia), and supportive care such as rest, fluids, and respiratory therapies. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for pneumonia is vital for managing this respiratory infection effectively and preventing its spread.
Causes of Pneumonia

Pneumonia is typically caused by the invasion of microbes into the lungs, leading to an infection. There are several different types of microorganisms that can cause pneumonia, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and certain parasites.
Bacterial Infections: Bacterial pneumonia is often caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, also known as pneumococcus. Other common bacteria that can cause pneumonia include Haemophilus influenzae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and Legionella pneumophila.
Viral Infections: Viral pneumonia is commonly caused by influenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and parainfluenza virus. These viruses can spread from person to person through respiratory droplets or by touching contaminated surfaces.
Fungal Infections: Fungal pneumonia is less common but can affect individuals with weakened immune systems or those exposed to certain environmental factors. Examples of fungi that can cause pneumonia include Pneumocystis jirovecii, Histoplasma capsulatum, and Cryptococcus neoformans.
Aspiration: Aspiration pneumonia occurs when foreign substances, such as food, liquids, or vomit, are inhaled into the lungs. This can lead to a localized infection and inflammation in the affected area.
Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP): VAP is a type of pneumonia that occurs in individuals who are on mechanical ventilation. It is often caused by bacteria that enter the lungs through the ventilator tube.
Understanding the causes of pneumonia can help in the prevention and effective treatment of this respiratory infection. Early identification and prompt treatment of the underlying cause are crucial to managing pneumonia effectively.
Understanding the Symptoms

Pneumonia can present with a variety of symptoms, which can range from mild to severe. It is crucial to recognize these symptoms and promptly seek medical attention. Some common symptoms of pneumonia include:
Cough: A persistent cough is often one of the first signs of pneumonia. The cough may produce phlegm or mucus, which can be yellow, green, or bloody.
Fever: Many individuals with pneumonia experience a high fever. This fever is frequently accompanied by chills and sweating.
Shortness of breath: Pneumonia can make it difficult to breathe, leading to shortness of breath or breathlessness. This symptom is more pronounced during physical activity or exertion.
Chest pain: Some people with pneumonia may experience chest pain, which can feel sharp or stabbing. The pain may worsen during coughing or deep breathing.
Fatigue: Pneumonia can cause fatigue and weakness, making individuals feel tired and lacking energy.
Loss of appetite: People with pneumonia often experience a loss of appetite due to the respiratory infection. This can contribute to weight loss and a general feeling of malaise.
It is important to note that symptoms can vary depending on the cause of pneumonia, the person's age, and overall health condition. In some cases, pneumonia can also lead to complications, such as confusion, bluish lips or nails (due to low oxygen levels), and rapid breathing.
If any of these symptoms are present, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment. Prompt medical attention can help prevent the progression of pneumonia and reduce the risk of complications.
Treatment Options
There are several treatment options available for pneumonia, depending on the severity of the infection and the individual's overall health. The primary goals of treatment are to eliminate the infection, alleviate symptoms, and prevent complications.
Antibiotics: Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to fight bacterial pneumonia. The type of antibiotic prescribed may vary based on the specific bacteria causing the infection. It is important to take the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed by the healthcare provider, even if symptoms improve, to ensure complete eradication of the bacteria.
Antiviral Medications: If the pneumonia is caused by a viral infection, antiviral medications may be prescribed. These medications can help reduce the severity and duration of the illness
.
Antipyretics: To reduce fever and alleviate discomfort, over-the-counter antipyretic medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be used. It is essential to follow the recommended dosage and consult a healthcare provider for appropriate use, especially for children and individuals with certain medical conditions.
Cough Medications: Over-the-counter cough medications can provide relief from a persistent cough. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any cough medication, as some may not be suitable for certain individuals or may interact with other medications.
Fluids and Rest: Getting plenty of rest and staying hydrated are crucial for the body to recover from pneumonia. Adequate fluid intake helps thin the mucus and facilitates its removal from the respiratory system.
Hospitalization: In severe cases of pneumonia, hospitalization may be necessary. This allows for close monitoring of the individual's condition and the administration of intravenous fluids, oxygen therapy, and additional treatments if required.
It is important to seek medical attention and follow the prescribed treatment plan for pneumonia. Prompt and appropriate treatment can help prevent complications and promote a faster recovery.
Pneumonia in Children and Elderly
Pneumonia can affect people of all age groups, but children and the elderly are particularly vulnerable to this respiratory infection.
Children:
1. Children, especially infants and young kids, are at a higher risk of developing pneumonia due to their developing immune systems.
2. Infections from viruses, bacteria, or fungi can cause pneumonia in children, and it is often transmitted through close contact with infected individuals.
3. Symptoms of pneumonia in children may include cough, fever, fast or difficult breathing, chest pain, decreased appetite, and fatigue.
4. Timely medical attention is crucial for children with pneumonia to prevent complications and ensure a speedy recovery.
5. Vaccination against pneumococcal infections and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) can significantly reduce the risk of pneumonia in children.
Elderly:
1. The elderly, especially those over the age of 65, are also more susceptible to pneumonia due to age-related changes in the immune system and underlying health conditions.
2. Pneumonia in the elderly is commonly caused by bacteria, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, or viruses like influenza.
3. Symptoms in the elderly may be less specific and can include confusion, shortness of breath, rapid breathing, weakness, and a decline in overall health.
4. Pneumonia can lead to severe complications in older adults, such as respiratory failure or sepsis, making prompt medical care essential.
5. Vaccination against pneumonia, including both pneumococcal and influenza vaccines, is recommended for elderly individuals to prevent infections and reduce the severity of illness.
Awareness of the vulnerability of children and the elderly to pneumonia is vital in ensuring prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Proper preventive measures, such as vaccination and hygiene practices, can significantly reduce the risk of pneumonia in these age groups.
What Our Patients Say

My father's Anjioplasty done successfully. This hospital is very expert hospital in cardiology. All doctors and other staff is very cooperative. Patient care is very nice. All medical facilities available. Good house keeping. Thanks.

My Pace maker procedure done successfully. All doctors and support staff is very cooperative. Patient care is very good. Nice housekeeping. Thanks.

This hospital is one of the best Cardiac care hospital in India. All doctors and support staff is very cooperative. My Anjiography and Anjioplasty done successfully. Patient care is very nice. House keeping is very good. Thanks to all.

This hospital is very best multi-speciality hospital. All doctors and staff is very cooperative. Patient care is very nice. Very best house keeping. Thanks.

Good people to take care of patients. Well managed and doctors do pay attention to the details. Friendly and helpful staff.My dad had a successful angioplasty here and I am hoping to have a follow up with degree of attention.I thank all the staff and doctors.

This hospital is very best multyspeciality hospital. My spinal fusion operation done succesfully. All doctors and staff is very nice. Paitent care is very good. Thanks.

My father's Anjiography and Angioplasty done successfully. This hospital is one of the best cardiac care hospital in India. All medical facilities available. All doctors and support staff is very cooperative. Patient care is very good. Thanks to all Saibaba team.

This hospital is one of the best cardiac care hospital in Maharashtra. All medical facilities available. All doctors and support staff is very expert. Patient care is very good. My Anjiography and Anjioplasty done successfully. Very good House keeping. Thanks to all..

My brother's Bye pass surgery done successfully. This hospital is very best cardiac care hospital in Nashik. All medical facilities available. Patients care is very nice. All doctors and staff is very cooprative. House keeping is very good. Thanks to all.

